936 字
5 分钟
pygame 北通手柄连接测试
前言
最近写了一个新的上位机控制端,但我发现使用键盘控制起来总有些便纽,不太方便,之前使用过PS2的手柄,通过一个单片机作为中继,然后上位机通过串口接收数据,但出现了不少问题。
首先是PS2手柄总是出现误触,其次单片机的处理和上位机的接收解析都提高了整体的输入延迟,之前看到有人使用XBOX直接连电脑发现效果不错,但苦于囊中羞涩,就买了个北通的,实际尝试下来发现还不错。
我购买的手柄是 北通斯巴达2游戏手柄-无线版,169块大洋,属于需要特定无线接收设备的那一类,兼容的是XBOX360模式,手感还是不错的。
系统版本:Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Ubuntu 上使用北通手柄
由于我这个北通手柄属于的是免驱动兼容XBOX手柄的类型,所以只需要按照XBOX手柄的安装方式,安装xboxdrv驱动1,可能提示信息:
Gimp with double *** has been moved to
可以不用管,回车继续即可:
sudo apt-apt-repository ppa:grumbel/ppasudo apt updatesudo apt install xboxdrv完成后打开手柄,输入如下指令,如果每次操作后数据有发生变化就说明连接成功:
cat /dev/input/jso hexdump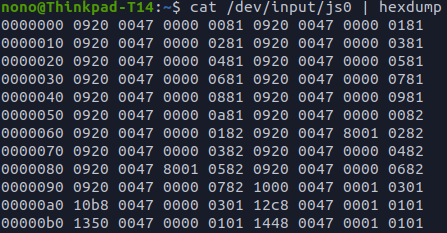
Ubuntu 安装 pygame
pygame 的安装方法和正常的python库相同,在终端中输入安装指令即可,这里给出两个方法,有1个能安装上就行:
sudo apt install python3-pygamesudo pip3 install pygame
通过 pygame 获取手柄输入
pygame安装完成后就能通过它给的一个案例获取手柄的输入信息2,案例是从pygame官网获取的,附在文章后面,官网可以直接访问。
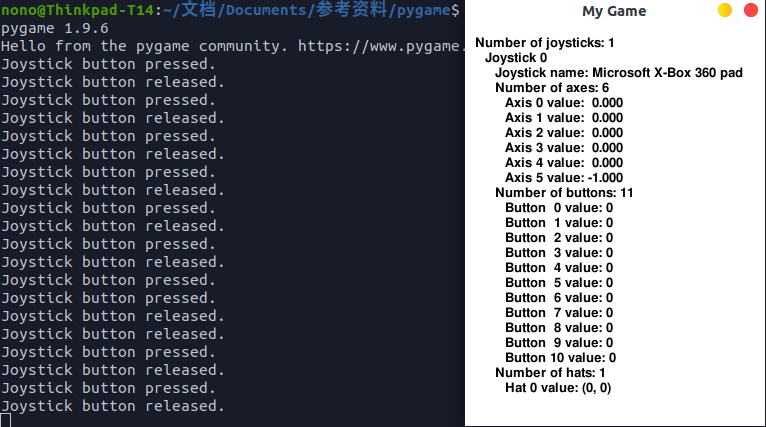
测试代码
# It has nothing to do with the joysticks, just outputting the# information.class TextPrint(object): def __init__(self): self.reset() self.font = pygame.font.Font(None, 20) def tprint(self, screen, textString): textBitmap = self.font.render(textString, True, BLACK) screen.blit(textBitmap, (self.x, self.y)) self.y += self.line_height def reset(self): self.x = 10 self.y = 10 self.line_height = 15 def indent(self): self.x += 10 def unindent(self): self.x -= 10pygame.init()# Set the width and height of the screen (width, height).screen = pygame.display.set_mode((300, 400))pygame.display.set_caption("My Game")# Loop until the user clicks the close button.done = False# Used to manage how fast the screen updates.clock = pygame.time.Clock()# Initialize the joysticks.pygame.joystick.init()# Get ready to print.textPrint = TextPrint()# -------- Main Program Loop -----------while not done: # # EVENT PROCESSING STEP # # Possible joystick actions: JOYAXISMOTION, JOYBALLMOTION, JOYBUTTONDOWN, # JOYBUTTONUP, JOYHATMOTION for event in pygame.event.get(): # User did something. if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # If user clicked close. done = True # Flag that we are done so we exit this loop. elif event.type == pygame.JOYBUTTONDOWN: print("Joystick button pressed.") elif event.type == pygame.JOYBUTTONUP: print("Joystick button released.") # # DRAWING STEP # # First, clear the screen to white. Don't put other drawing commands # above this, or they will be erased with this command. screen.fill(WHITE) textPrint.reset() # Get count of joysticks. joystick_count = pygame.joystick.get_count() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Number of joysticks: {}".format(joystick_count)) textPrint.indent() # For each joystick: for i in range(joystick_count): joystick = pygame.joystick.Joystick(i) joystick.init() try: jid = joystick.get_instance_id() except AttributeError: # get_instance_id() is an SDL2 method jid = joystick.get_id() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Joystick {}".format(jid)) textPrint.indent() # Get the name from the OS for the controller/joystick. name = joystick.get_name() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Joystick name: {}".format(name)) try: guid = joystick.get_guid() except AttributeError: # get_guid() is an SDL2 method pass else: textPrint.tprint(screen, "GUID: {}".format(guid)) # Usually axis run in pairs, up/down for one, and left/right for # the other. axes = joystick.get_numaxes() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Number of axes: {}".format(axes)) textPrint.indent() for i in range(axes): axis = joystick.get_axis(i) textPrint.tprint(screen, "Axis {} value: {:>6.3f}".format(i, axis)) textPrint.unindent() buttons = joystick.get_numbuttons() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Number of buttons: {}".format(buttons)) textPrint.indent() for i in range(buttons): button = joystick.get_button(i) textPrint.tprint(screen, "Button {:>2} value: {}".format(i, button)) textPrint.unindent() hats = joystick.get_numhats() textPrint.tprint(screen, "Number of hats: {}".format(hats)) textPrint.indent() # Hat position. All or nothing for direction, not a float like # get_axis(). Position is a tuple of int values (x, y). for i in range(hats): hat = joystick.get_hat(i) textPrint.tprint(screen, "Hat {} value: {}".format(i, str(hat))) textPrint.unindent() textPrint.unindent() # # ALL CODE TO DRAW SHOULD GO ABOVE THIS COMMENT # # Go ahead and update the screen with what we've drawn. pygame.display.flip() # Limit to 20 frames per second. clock.tick(20)# Close the window and quit.# If you forget this line, the program will 'hang'# on exit if running from IDLE.pygame.quit()Footnotes
pygame 北通手柄连接测试
https://fuwari.vercel.app/posts/编程/python/pygame-获取手柄信息/ 